Guida SEO per l'e-commerce:in che modo i negozi online possono guidare il traffico organico nel 2022
Questa è la guida più completa all'e-commerce SEO sul web – punto.
Che tu sia:
- Il SEO manager di una grande azienda di e-commerce che cerca di dimostrare il ROI della SEO.
- Un piccolo imprenditore online che cerca di trovare modi frammentari per far crescere la tua attività.
- O un marketer in crescita alla ricerca di modi innovativi e altamente efficaci per aumentare il traffico.
Questo post è per te.
Ho creato questa guida per un motivo...
L'ottimizzazione per i motori di ricerca è un vantaggio per i siti di e-commerce.
Nonostante il SEO abbia il ROI più alto di qualsiasi campagna di marketing per l'e-commerce, la maggior parte dei negozi online viene messa insieme con poca o nessuna considerazione dei motori di ricerca.
Invece, ci affidiamo ai social media o agli annunci a pagamento. Che sono fantastici e tutti, ma richiedono uno sforzo e un flusso di entrate costanti.
La SEO, d'altra parte, richiede solo uno sforzo in anticipo:una volta che ti classifichi, fai praticamente vendite con il pilota automatico senza spese ricorrenti.
Questa è una semplificazione, ovviamente. Ma l'idea non ti fa sbavare?
Traffico gratuito, ricorrente e ad alta conversione. Questo è ciò che stai per imparare a ottenere.
Prendi un caffè, chiudi a chiave la porta e sistemati... è tempo di imparare l'e-commerce SEO.
Naturalmente, se sei un commerciante di BigCommerce, puoi programmare un po' di tempo con il nostro team per saperne di più sul coaching SEO della BigCommerce University.
Tattiche chiave da includere nella tua strategia SEO per l'e-commerce
Dato che questa è una bestia di 9.000 parole, probabilmente vorrai prenderla una sezione alla volta. Per aiutarti a navigare, ecco gli argomenti che tratteremo.
La migliore strategia SEO per l'e-commerce include:
- Ricerca di parole chiave per trovare i tipi di parole chiave che i clienti stanno cercando.
- Architettura del sito basata sulla ricerca di parole chiave.
- Seo on-page attraverso l'ottimizzazione strategica delle parole chiave nei meta tag e nei contenuti.
- Seo tecnico per garantire che i motori di ricerca possano eseguire la scansione del tuo sito in modo efficiente.
- Seo locale per aiutare a guidare il traffico organico locale (se hai un mattone e malta).
- Il marketing dei contenuti per aumentare i visitatori organici.
- Link Building per migliorare l'autorevolezza del tuo sito web.
- Misurare il successo SEO con strumenti come Google Analytics e Ahrefs.
Iniziamo!
Cos'è la SEO e perché dovrebbe interessarti?
L'ottimizzazione per i motori di ricerca (SEO) è l'arte scientifica di ottimizzare il tuo sito Web in base a parole chiave specifiche per posizionarsi più in alto nei risultati di ricerca, come Google.
Dico arte scientifica perché, mentre si sa molto sugli aspetti tecnici della SEO, c'è anche un'esperienza utente creativa e un lato del design.
Ma ottimizzare il tuo sito, in definitiva, significa una cosa:creare il miglior risultato possibile per la tua parola chiave target.
L'obiettivo di Google è classificare i risultati di ricerca che rispondono così bene a tutte le domande degli utenti che non hanno bisogno di tornare su Google per un'altra risposta.
Allora come si fa?
- Rivela le risposte più esaurienti alla più ampia gamma di domande sull'argomento.
- Utilizza immagini, video o esempi migliori per spiegare i tuoi punti.
- Fornire una migliore esperienza utente tramite un sito più veloce, una migliore esperienza mobile, un'interfaccia più intuitiva, ecc.
- Fai in modo che le persone parlino (e si colleghino) a te.
Uno studio di Outbrain mostra che la ricerca è il principale motore di traffico verso i siti di contenuti, battendo i social media di oltre il 300%.
Inoltre, uno studio di SEMrush che ha esaminato 13 verticali di e-commerce ha rilevato che 5 (musica, libri, mobili, casa e giardino, elettronica) erano dominati dalla ricerca organica e per tutti e 13 organici e diretti rappresentavano l'80% di tutto il traffico.
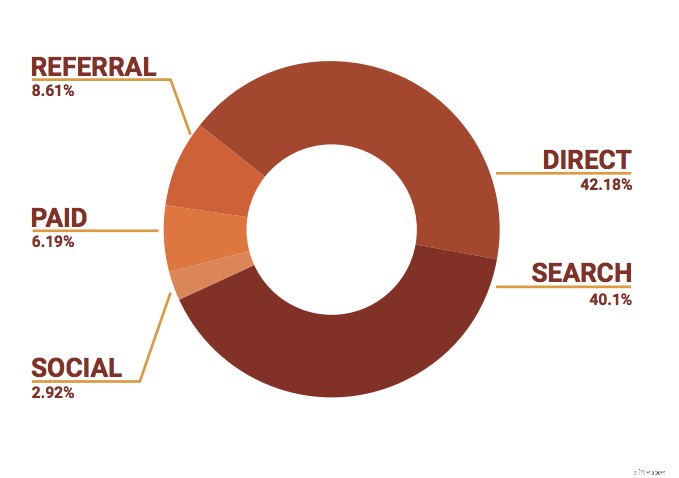
Fonti di traffico del sito e-commerce tramite SEMrush
Per l'e-commerce, ciò significa scrivere descrizioni di prodotti complete e vivide con fotografie belle e accattivanti e numerose recensioni per aiutare i visitatori a prendere decisioni di acquisto.
Significa anche semplificare l'acquisto da parte dei visitatori rendendo i pulsanti sufficientemente grandi, mantenendo il tuo sito privo di problemi e mostrando social proof dei tuoi migliori prodotti.

Oh, e significa offrire ai visitatori del tuo sito confronti del tuo prodotto con i tuoi concorrenti, in modo che non debbano andarsene per fare ulteriori ricerche.
Ma ne parleremo più avanti. Per ora, voglio solo che tu capisca una cosa:
La SEO è uno sforzo olistico di tutte le parti di un'azienda, inclusi social media, marketing, web design, networking e copywriting.
Se sei il miglior affare per un cliente per fare acquisti (e fai i tuoi compiti SEO) rivendicherai le prime posizioni. Non è fantastico quanto sia semplice?
Ma non ho risposto alla domanda più importante... Perché dovrebbe interessarti?
Bene, supponiamo che il tuo negozio venda regali per gli amanti dei cani wiener, come il mio cliente, The Smoothe Store. Ovviamente, vorresti classificarti per un termine chiave come "Regali per bassotto".
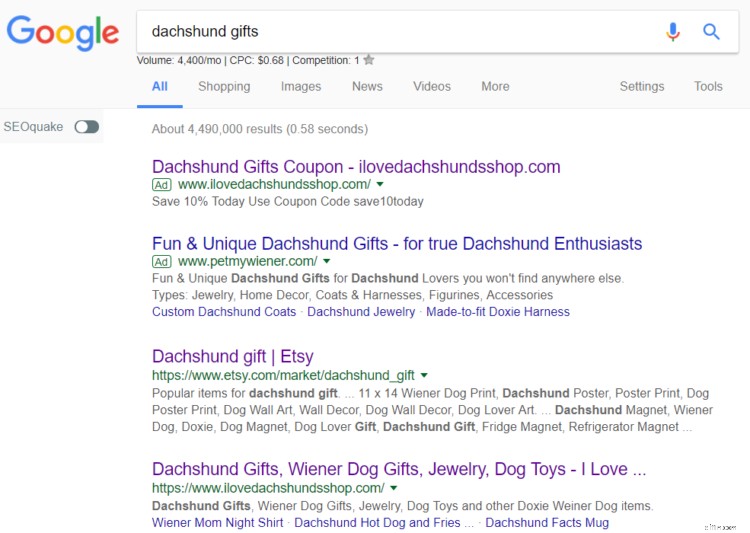
Nei risultati di ricerca, Google mostra alcuni annunci, quindi mostrano gli elenchi organici. La maggior parte dei clic, tuttavia, va a risultati organici. (Ovviamente, questo varia a seconda del numero di annunci e della parola chiave, ma per la maggior parte è vero.)
E poiché circa il 95% delle persone non va oltre la prima pagina, arrivare in cima alla linea è l'unico modo per ottenere risultati reali. (Di nuovo, questo varia, ma per lo più vale.)
Ora facciamo un po' di calcoli.
La parola chiave "Regali bassotto" riceve in media circa 11.000 ricerche al mese, secondo Ahrefs (uno strumento che imparerai in una sezione successiva). Supponendo che il 35% di quei clic vada al primo risultato (la media tra le parole chiave), posizionarsi al primo posto per quella parola chiave ti farebbe ottenere 3.850 clic.
Ora supponiamo che tu abbia un tasso di conversione del 10% (abbastanza basso per una parola chiave con un forte intento dell'acquirente; maggiori informazioni sull'intento dell'acquirente nella sezione di ricerca).
La classifica #1 per quella parola chiave ti farebbe guadagnare 385 vendite extra al mese!

E questa è solo una parola chiave. La maggior parte delle pagine viene classificata per più parole chiave e la maggior parte dei siti classifica più pagine.
Potresti ottenere migliaia di vendite extra al mese con un piccolo sforzo SEO in più, il tutto gratuitamente.
Potresti anche combinare SEO con SEM (marketing sui motori di ricerca, come Google AdWords) per ottenere due elenchi di risultati di ricerca e convertire ancora più vendite. Ma questo è un argomento per un'altra guida. (Tuttavia, se sei interessato agli annunci a pagamento, dai un'occhiata ai servizi PPC di KlientBoost.)
Spero che ormai tu capisca perché Google è uno dei migliori canali di marketing.
Ma basta teoria:parliamo di come farlo davvero!
Ricerca per parole chiave e-commerce
La ricerca per parole chiave è il primo passo in una campagna SEO e-commerce.
NON saltare questo passaggio.
Se sbagli questa parte, accadrà una di queste due cose:
- Ti rivolgerai a parole chiave troppo difficili da classificare e non arriverai alla prima pagina.
- Ti classificherai per le parole chiave che non ottengono molto traffico o non inducono i clienti ad acquistare.
Nessuna di queste situazioni è l'ideale, motivo per cui la ricerca di parole chiave per l'e-commerce è così importante:ti assicurerà di scegliere come target parole chiave che sono abbastanza facili da classificare, hanno un volume di ricerca decente e hanno tassi di conversione elevati.
Ma c'è di più nella scelta delle parole chiave che semplicemente guardare quanto sia difficile classificarsi o quante persone le cercano...
Per scegliere le migliori parole chiave possibili, devi anche tenere conto dell'intenzione dell'acquirente (nota anche come "intenzione commerciale").
Questo è così importante, lo stiamo mettendo in una scatola in modo da non perderlo (seriamente)
L'intenzione dell'acquirente significa semplicemente fino a che punto qualcuno è nella sua decisione di acquistare.
Ad esempio, qualcuno che cerca il "miglior laptop" è probabilmente ancora nella fase di ricerca:potrebbe non essere pronto per l'acquisto. È probabile che leggano le recensioni dei prodotti e confrontino caratteristiche e vantaggi.
Ma se stanno cercando "Asus VivoBook E200HA", probabilmente stanno cercando l'offerta migliore su quel laptop esatto, il che significa che è molto più probabile che acquistino.
Non devi indovinare l'intenzione dell'acquirente.
Spesso, l'intento dell'acquirente è correlato al costo medio per clic (CPC) di una parola chiave, che può essere trovato con Google Keyword Planner o uno strumento SEO come Ahrefs. Questo perché più persone sono disposte a spendere per pubblicizzare una parola chiave, maggiore è il suo tasso di conversione!
Suggerimento per professionisti: "Il miglior prodotto X" è un'ottima idea potenziale per il tuo blog. Maggiori informazioni sui blog nella sezione marketing dei contenuti.
Ora probabilmente ti starai chiedendo:come esegui la ricerca di parole chiave e-commerce, trovi la difficoltà delle parole chiave (KD) e il volume di ricerca e scopri l'intenzione dell'acquirente?
Bene, ci sono tre modi:
- Amazon
- Ricerca sulla concorrenza
- Strumenti SEO
Cominciamo con il colosso dell'e-commerce.
1. Usa Amazon per la ricerca di parole chiave.
Amazon è una miniera d'oro di parole chiave ad alto intento di acquisto:le persone cercano letteralmente su Amazon con l'intento di acquistare qualcosa.
Per trovare parole chiave con Amazon, inizia a digitare la tua parola chiave seed. Questa è una parola per la quale pensi che probabilmente ti piacerebbe classificarti.
Ad esempio, potremmo digitare "Dachshund"...

…e Amazon sputa suggerimenti di riempimento automatico come regali per bassotti, magliette, peluche, ecc. Queste sono tutte idee per le parole chiave:inseriscile in un foglio di lavoro di Google per conservarle in seguito.
Come puoi immaginare, se hai centinaia o migliaia di prodotti, questo potrebbe richiedere molto tempo. È qui che entra in gioco Amazon Keyword Tool.
Questo pratico strumento analizza automaticamente i suggerimenti di compilazione automatica di Amazon per qualsiasi parola chiave digitata. Ti offre tre ricerche gratuite al giorno, quindi non devi spendere nulla.
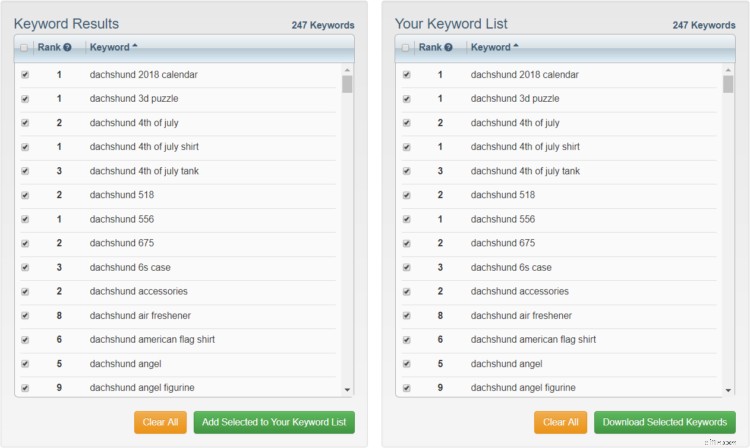
Semplicemente digitando e cercando "Dachshund", ora ho 247 parole chiave potenzialmente ad alto intento di acquisto. Woohoo!
Puoi ripetere questa operazione per tutte le tue parole chiave seed (come "cane salsiccia" invece di bassotto).
Ogni volta che esegui una ricerca, seleziona tutte le parole chiave e aggiungile all'elenco, quindi scarica l'elenco in un CSV con il pulsante "Scarica parole chiave selezionate".
Tuttavia, non possiamo semplicemente scegliere ciecamente queste parole chiave. Dobbiamo ancora capire il volume di ricerca, la difficoltà e persino l'intenzione dell'acquirente prima di scegliere quelli che utilizziamo nel nostro negozio.
Ma per ora, parliamo di altri modi per trovare altre idee per le parole chiave.
2. Trova le parole chiave attraverso la ricerca della concorrenza.
Se hai concorrenti che si posizionano più in alto di te nei risultati di ricerca, puoi utilizzare il loro sito per rubare idee per le parole chiave.
Avviso spoiler
La prossima sezione mostra come farlo in meno di 5 minuti usando Ahrefs. Ma per quelli di voi che non utilizzeranno lo strumento, continuate a leggere!
Innanzitutto, digita la tua parola chiave in Google...
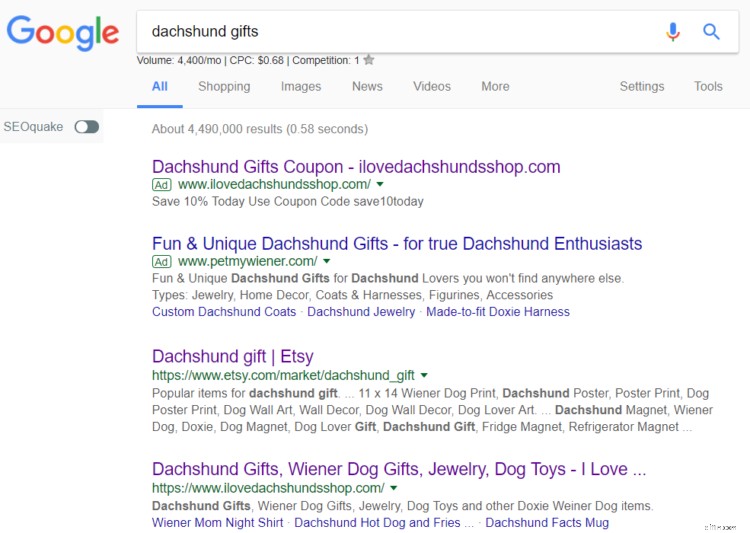
…scegli un concorrente…
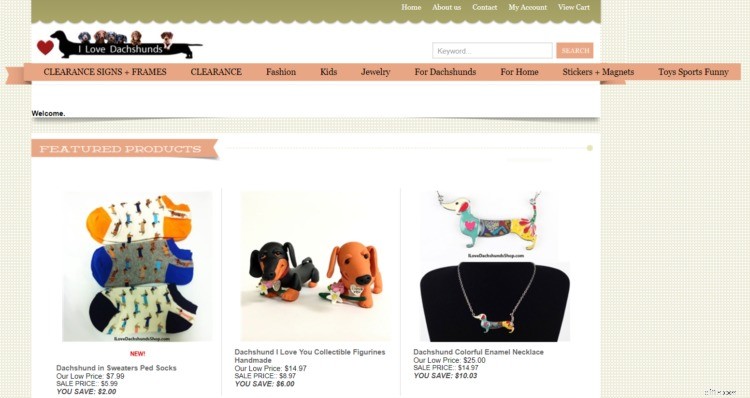
...e scansiona la loro categoria e le pagine dei prodotti alla ricerca di potenziali parole chiave.
Tuttavia, NON utilizzare ciecamente le stesse parole chiave del tuo concorrente! Solo perché ti superano, non significa che abbiano scelto le migliori parole chiave:potrebbero semplicemente avere un'autorità di dominio (DA) più alta di te.
Buono a sapersi
DA è il grado della società SEO Moz di quanto sia autorevole un sito Web, in base al suo profilo di collegamento e ad altri fattori (ad esempio il numero di backlink che puntano a un sito da un altro sito).
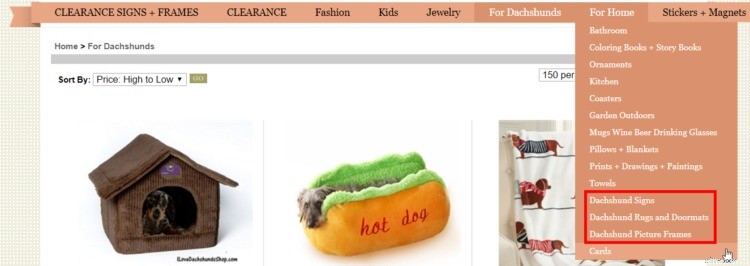
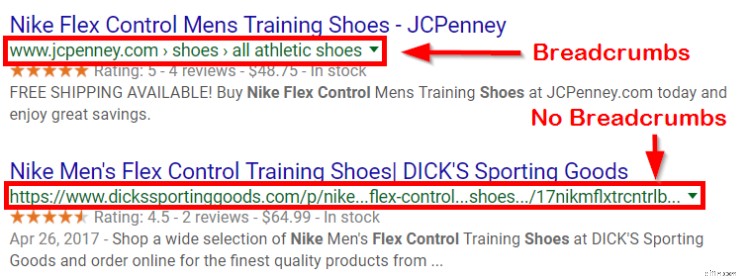
Suggerimento per professionisti:questo è un buon momento per menzionare i breadcrumb, una funzione di navigazione avanzata che aiuta Google a scansionare e indicizzare il tuo sito.
Puoi sapere se hai impostato correttamente i breadcrumb inserendo il tuo sito in Google. Se vedi "tuosito.com -> categoria -> sottocategoria", hai impostato i breadcrumb. Maggiori informazioni qui.
Per ora, registra le parole chiave nel tuo foglio e vai avanti.
3. Usa Ahrefs per aiutarti a trovare opportunità di parole chiave.
Ahrefs, lo strumento che ho menzionato sopra, è uno straordinario strumento SEO a tutto tondo. Puoi usarlo per la ricerca di parole chiave, la ricerca competitiva, per creare backlink e molto altro.
E arriveremo a tutto questo, ma per ora parliamo di come utilizzarlo per eseguire facilmente e rapidamente ricerche di parole chiave e-commerce.
Dopo aver creato un account (ottieni una prova gratuita di due settimane), inserisci il tuo URL nella barra di ricerca di Site Explorer. Lo esaminerò usando il mio sito, The Wandering RV, come esempio.
Fai clic sulla scheda "Ricerca organica"...
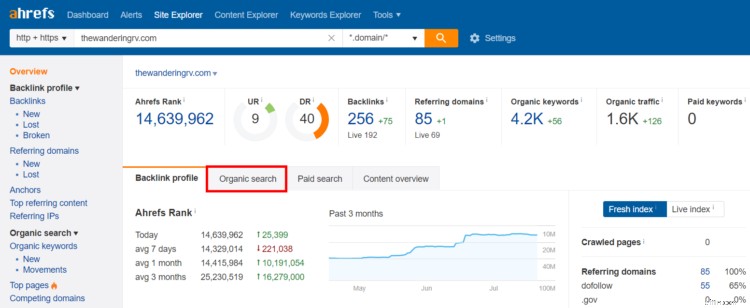
…scorri verso il basso e fai clic su "Visualizza rapporto completo" nella sezione delle 5 principali parole chiave organiche...
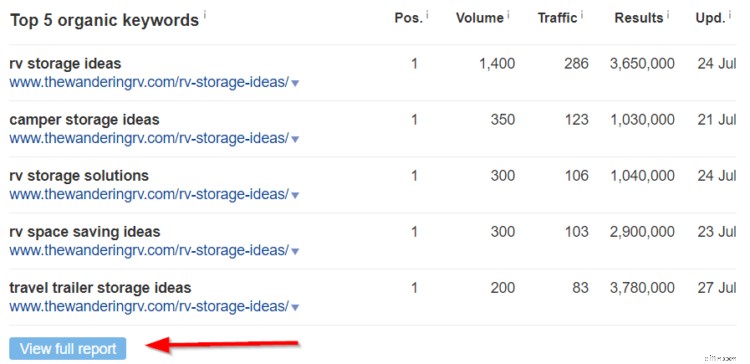
... e vedrai tutte le parole chiave per le quali si posiziona il tuo sito.
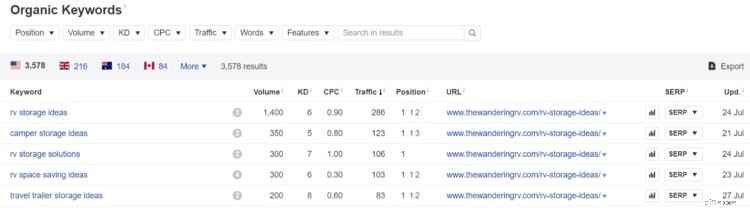
Nel mio caso, 3.578 parole chiave. Più di quanto mi interessi scavare uno per uno.
Fortunatamente, puoi filtrare i risultati per ottenere esattamente quello che stai cercando. In particolare, voglio trovare il mio frutto basso; le parole chiave per le quali mi classifico dal 5 al 10.
Questi sono frutti a basso impatto perché sei già sulla prima pagina, il che significa che dovrebbe essere abbastanza facile posizionarsi più in alto con una corretta SEO on-page e forse anche un po' di link building (maggiori informazioni su SEO on-page e link sezioni edilizie).
Per trovarli, filtra per Posizione:minimo 3 e massimo 10.
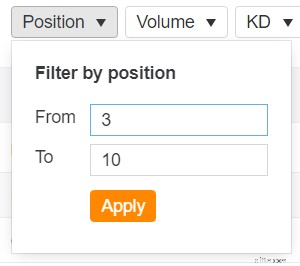
Puoi anche ordinarlo in base al traffico in ordine decrescente semplicemente facendo clic sulla colonna Traffico. Se lo desideri, puoi anche inserire un filtro di traffico minimo, ad esempio non meno di 200 ricerche al mese. Non ne ho molti, quindi non lo farò.
Ora, esporta le tue parole chiave a basso contenuto di frutta in un CSV con il pulsante "Esporta" in alto a destra e copiale e incollale in una nuova scheda nel foglio di lavoro. (Chiamo questa scheda "Frutta a basso impatto".)

Ora rubiamo le parole chiave dei nostri concorrenti.
Digita un concorrente nello strumento di esplorazione del sito questa volta e vai alla stessa pagina delle parole chiave organiche. Per trovare le pepite d'oro, applica questi filtri:
- Posizione max 20
- KD max 15
- Volume minimo 200
Questo ti mostrerà tutte le parole chiave pertinenti a bassa difficoltà per le quali il tuo concorrente si classifica! Quanto è fantastico?
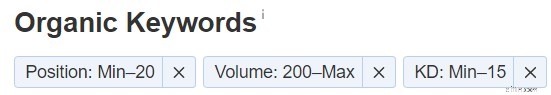
Sentiti libero di rimuovere il volume minimo se non ottieni risultati sufficienti:alcune nicchie non avranno un volume di ricerca elevato. Lo faccio solo per mantenere il massimo potenziale di parole chiave e per mantenere il numero totale gestibile.
Va bene, probabilmente stai affogando nelle idee per le parole chiave ora, ma ne ho una in più per te:lo strumento per il divario dei contenuti.
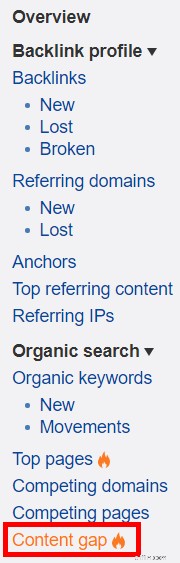
Questo strumento ingegnoso ti mostra tutte le parole chiave per le quali i tuoi concorrenti si classificano ma tu no. Digita tre (o più) concorrenti nei primi tre campi e il tuo sito in basso.
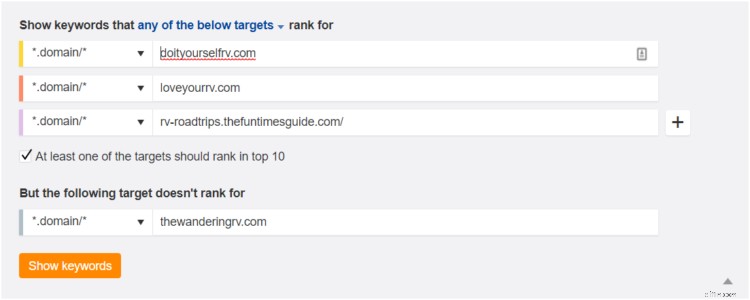
Quindi premi "Mostra parole chiave" per essere inondato di opportunità! Basta applicare i filtri come abbiamo fatto sopra per trovare quelli davvero fantastici, quindi esportarli e incollarli nel foglio di lavoro.
Quindi ora che sei all'altezza delle idee sui termini chiave, come fai a sapere quali utilizzare effettivamente?
4. Determina se stai scegliendo le parole chiave giuste.
A meno che tu non abbia utilizzato Ahrefs, non avrai dati sulle parole chiave per le frasi che hai scelto. Devi determinare la difficoltà delle parole chiave, il volume di ricerca e l'intenzione dell'acquirente per sapere quali parole chiave utilizzare.
Puoi trovare il volume di ricerca approssimativo e il CPC (per determinare l'intento dell'acquirente) utilizzando lo Strumento di pianificazione delle parole chiave di Google. Tuttavia, non ti dà difficoltà con le parole chiave (non lasciarti confondere dalla concorrenza:è solo concorrenza per annunci AdWords a pagamento, non ranking organico).
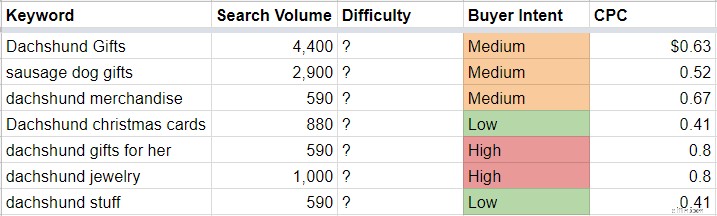
Facciamo una ricerca per i regali di Bassotto...
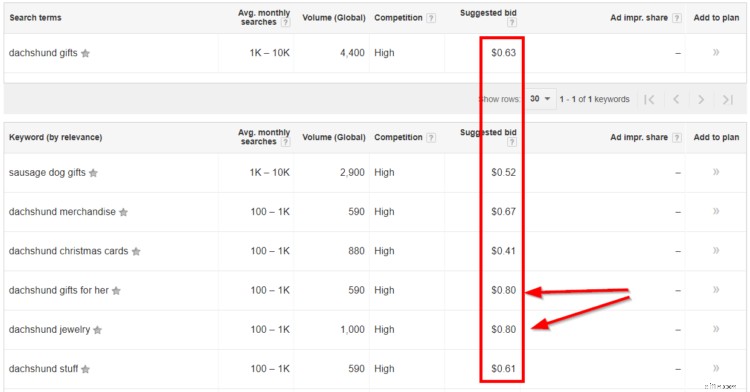
L'"offerta consigliata" è il CPC. Un CPC elevato indica un'elevata intenzione dell'acquirente, come abbiamo discusso.
Quello che stai cercando qui è un CPC elevato rispetto ad altri CPC:in alcune nicchie, $ 0,80 potrebbe essere un affare. In altri (come i regali del bassotto), $ 0,80 sono molti soldi. La relatività è fondamentale.
Prendi nota del volume e dell'intento dell'acquirente nel tuo foglio per tutte le tue parole chiave molto importanti.
Osservalo semplicemente su "basso", "medio" o "alto" in base al suo CPC in relazione al CPC generale che vedi nella maggior parte delle parole chiave nella tua nicchia.
Ad esempio, classificherò le parole chiave dall'immagine dello Strumento di pianificazione delle parole chiave di Google sopra:
Ovviamente, Ahrefs lo fa automaticamente per te (meno l'intenzione dell'acquirente), quindi preferisco di gran lunga quella strada. Ma non è gratuito dopo il periodo di prova, quindi questo è il vero metodo bootstrap.
Suggerimento professionale
Puoi anche trovare ottime parole chiave spiando le offerte AdWords dei tuoi concorrenti. Basta eseguire alcune analisi PPC competitive e aggiungerle al tuo foglio!
Una volta terminato, ordina i risultati in base al miglior mix di traffico, KD e intenzione dell'acquirente. Queste sono le parole chiave a cui vuoi dare più priorità.
Tuttavia, se vuoi DAVVERO prendere sul serio la tua SEO e massimizzare la diffusione delle tue parole chiave, dovresti prendere in considerazione la creazione di una matrice di parole chiave.
Una matrice di parole chiave è fondamentalmente un modo per esaminare tutte le tue parole chiave e organizzare il tuo foglio di calcolo per determinare rapidamente le migliori parole chiave possibili da utilizzare su ciascuna delle tue pagine. Si basa su KD, volume di ricerca e intento di ricerca (cosa cercano le persone quando effettuano una ricerca particolare).
Se è qualcosa che ti interessa, puoi leggere di più qui o assumermi per farlo per te.
Basta con la ricerca di parole chiave per il tuo sito di e-commerce... parliamo di come usarle!
Architettura del sito di e-commerce
Una volta che conosci le parole chiave giuste per il targeting, è il momento di mettere in pratica tali informazioni.
Questo inizia con l'architettura del tuo sito.
L'architettura o la struttura del sito di e-commerce è il modo in cui imposti la navigazione, le pagine delle categorie e le pagine dei prodotti. Fondamentalmente, si tratta di ottenere i contenuti migliori e più pertinenti davanti agli utenti e di ridurre il numero di volte in cui devono fare clic per trovarli.
Esistono due "regole d'oro" per un'ottima struttura del sito:
- Rendilo semplice e scalabile.
- Nessuna pagina dovrebbe richiedere più di tre clic per arrivare da qualsiasi altra pagina.
- Utilizza la ricerca per parole chiave per creare URL di pagina e sottodirectory altamente pertinenti.
Ne parleremo più avanti:per ora, parliamo di cosa NON fare.
Un esempio di architettura del sito BAD per un sito di e-commerce
Ecco come appare l'architettura del sito scadente:
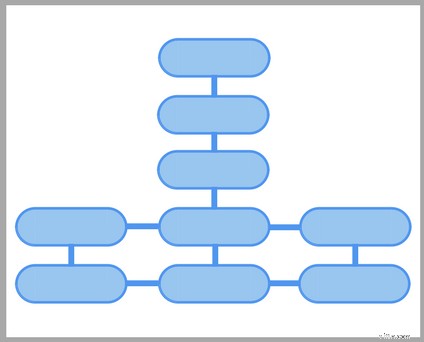
Rompe entrambe le regole d'oro. Bastano quattro clic per arrivare a una pagina di categoria e, se vuoi aggiungere una pagina di prodotto o categoria, devi nasconderla nelle viscere del tuo sito.
Non solo è scadente per la navigazione, ma danneggia anche le classifiche di ricerca. Ecco perché:
In genere, la tua home page è la pagina più autorevole del tuo sito. I collegamenti interni da una pagina all'altra del tuo sito trasmettono parte di quel "succo di collegamento" o "autorità" da una pagina all'altra. In precedenza si chiamava PageRank, ma Google non utilizza più quel termine.
Visivamente, funziona così:

Quindi la tua home page può trasferire la maggior parte dell'autorità alle pagine delle tue categorie, che poi passano l'autorità alle pagine dei tuoi prodotti.
Visto in un altro modo, funziona così:
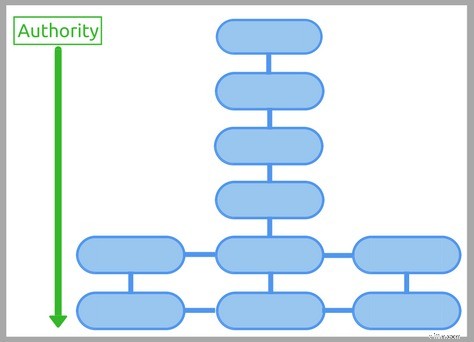
Per darti un'analogia, pensa alla struttura del tuo sito web come al sistema di irrigazione di una fattoria e all'autorità del sito o "succo di collegamento" come l'acqua della fattoria. Le tue pagine sono le piante.
Ovviamente, vuoi dare più acqua alle piante più produttive:la tua categoria principale e le pagine dei prodotti.
Per farlo, devi inviare loro i link più interni dalle tue pagine di massima autorità, cosa che questo cattivo esempio non sta facendo.
Questo è anche un buon momento per menzionare il content marketing. Grandi contenuti possono fungere da impianti più grandi, ricevendo un sacco di backlink esterni da altri siti. Puoi quindi incanalare l'autorità di collegamento dai tuoi contenuti alle pagine dei tuoi prodotti e categorie. Acqua gratis! (Maggiori informazioni su questo nella sezione "marketing dei contenuti e-commerce".)
Ora vediamo come è fatto.
Suggerimento professionale
Se il tuo sito ha già una struttura tutt'altro che ideale, non spostarti tra le pagine prima di aver consultato un esperto SEO. Possiamo aiutarti a consolidare le pagine, migliorare i collegamenti interni e reindirizzare le vecchie pagine a nuove pagine senza danneggiare il tuo SEO.
Un esempio di BUONA architettura del sito di e-commerce
Per ottenere la massima autorità dalle tue pagine migliori, inizia con la struttura del tuo sito. E ricorda le regole d'oro (semplice e scalabile, non più di 3 click)!
(Pssst! I negozi realizzati con BigCommerce lo fanno automaticamente.)
Un buon sito sarebbe simile a questo:
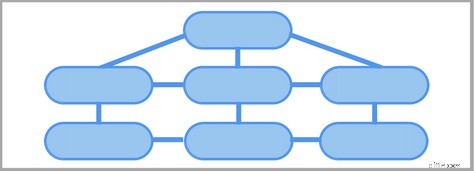
La tua home page dovrebbe collegarsi a tutte le pagine delle tue categorie principali e potenzialmente anche ad alcune delle migliori pagine dei tuoi prodotti.
La corretta navigazione e il collegamento interno assicurano che quelle pagine ottengano la massima autorità dalla tua home page e quindi abbiano maggiori possibilità di posizionarsi in alto nelle ricerche.
Per darti un'idea migliore, dai un'occhiata alla home page che ho creato per il mio cliente, The Smoothe Store.
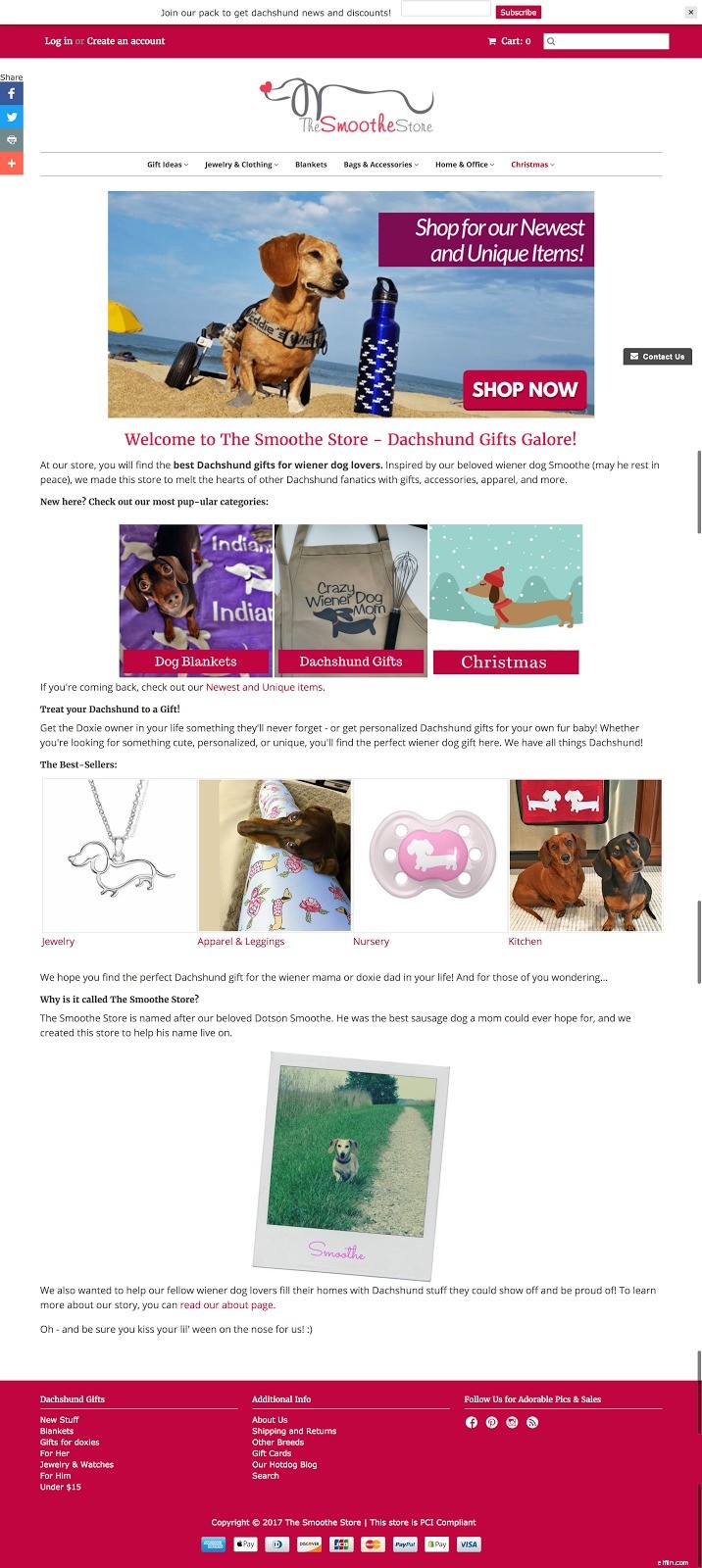
Come puoi vedere, ci colleghiamo a tutte le nostre pagine di categoria superiore. Lo facciamo anche visivamente, rendendolo più accattivante e facile da navigare.
Un'altra cosa che sottolineerò è tutto il contenuto del testo:avere contenuti sulla tua home page aumenta le tue classifiche. Ma di più su questo nella sezione SEO in pagina qui sotto.
Suggerimento professionale
Assicurati di includere una sezione "prodotti correlati" in ogni pagina di prodotto. Ciò aggiungerà collegamenti interni più rilevanti e ha dimostrato di aumentare il valore medio dell'ordine.
Una strategia SEO on-page per i siti di e-commerce
La SEO on-page per l'e-commerce consiste nell'assicurarsi che le tue parole chiave siano nei posti giusti. È solo un modo per garantire che Google sappia esattamente di cosa tratta la tua pagina.
Stiamo per discutere tre strategie:
- SEO on-page per le pagine di categoria eCommerce.
- SEO on-page per le pagine dei prodotti eCommerce.
- SEO on-page per i contenuti del tuo blog.
La SEO on-page è importante perché ti aiuta anche ad apparire in altre funzionalità della pagina dei risultati dei motori di ricerca (SERP).
SEMrush ha scoperto che i siti Web di e-commerce dovrebbero concentrarsi su recensioni e immagini.
Per le 15 funzionalità analizzate (l'ultima è l'assenza di funzionalità SERP), le recensioni sono state le prime nel 57,93% delle ricerche globali e nel 62,03% delle ricerche negli Stati Uniti.
Anche le immagini sono state importanti e hanno superato i risultati video visualizzati nel 51,09% delle ricerche globali e nel 41,68% delle ricerche negli Stati Uniti.
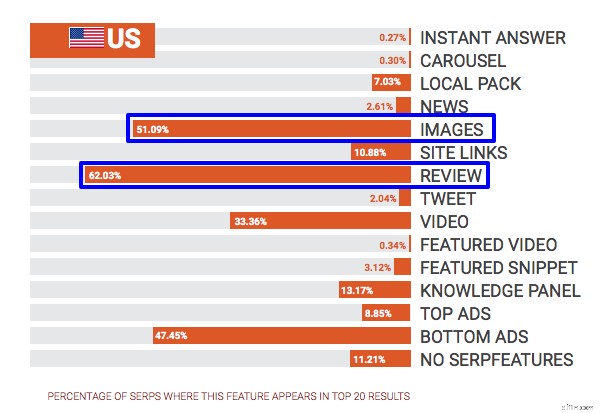
Le principali funzionalità SERP statunitensi dallo studio SEMrush
Diamo un'occhiata a tutti i fattori di ranking per SERP.
14 Funzionalità SERP di Google
- Risposta immediata. In genere viene visualizzata nella parte superiore della pagina dei risultati, ma sotto gli annunci, è presente una casella con una breve risposta di testo e un URL di origine.
- Carosello. Questi mostrano risultati locali con un'immagine, il nome dell'attività, valutazioni e recensioni.
- Pacchetto Locale. Mostra, in genere 3, attività commerciali locali e una mappa di Google ed è dominante sui dispositivi mobili.
- Notizie. Un blocco di argomenti di notizie sensibile al tempo che appare nella parte superiore della pagina dei risultati.
- Immagini. Questi mostrano una riga orizzontale di immagini nella parte superiore di una ricerca.
- Link al sito. Per la ricerca sull'intento del marchio, possono essere visualizzati fino a 10 link a siti insieme a un risultato organico.
- Recensione. Questo risultato multimediale (precedentemente chiamato rich snippet) mostra stelle e dati di valutazione per prodotti e altri articoli a cui è possibile aggiungere recensioni.
- Tweet. I tweet pertinenti possono apparire nei risultati organici.
- Video. I video di YouTube, Vimeo e altre piattaforme possono essere visualizzati con la loro miniatura nei risultati organici.
- Video in primo piano. Ha una miniatura più grande e può fornire più informazioni e viene visualizzata nella parte superiore dei risultati di ricerca.
- Snippet in primo piano. Una casella speciale che risponde a una domanda specifica e viene visualizzata sopra i primi risultati organici.
- Riquadro della conoscenza. Utilizza i dati semantici da varie fonti per visualizzare il blocco di informazioni su persone, film ed eventi per citarne alcuni elementi e di solito appare a destra dei risultati di ricerca.
- Annunci principali. Annunci AdWords che occupano i primi 4 posti nella pagina di ricerca.
- Annunci inferiori. Annunci AdWords che occupano gli ultimi 3 posti nella pagina di ricerca.
Iniziamo come inserire ciascuno di questi fattori nel tuo Santo Graal:le pagine delle tue categorie.
2. Implementa la SEO on-page per le pagine dei prodotti e-commerce.
Le pagine delle tue categorie sono probabilmente le pagine più importanti da classificare. Se qualcuno li trova su Google, ha immediatamente accesso a tutti i tuoi prodotti in quella categoria.
Per ottimizzare correttamente queste pagine, devi inserire la tua parola chiave target nei seguenti posti:
1. Nell'URL.
Inserire la tua parola chiave principale nell'URL (e rendere l'URL leggibile e comprensibile) è semplice e migliora il posizionamento nei risultati di ricerca.

Degno di nota anche: vedi "/collections/" nell'URL? In realtà è un male per la SEO (e una limitazione di Shopify). Google preferisce URL più brevi e più facili da leggere, quindi questa parola aggiuntiva ha un impatto negativo sulla SEO.
Fortunatamente, BigCommerce ti consente di rimuovere queste sottocartelle extra dal tuo URL in modo rapido e semplice.
Ciò è particolarmente rilevante per i siti Web che competono in nicchie più competitive. Ci sono molti fattori associati alle classifiche organiche; tuttavia, gli URL ottimizzati sono un ulteriore modo per ottenere un vantaggio sulla concorrenza per aumentare il traffico.
Puoi anche personalizzarli in base a qualsiasi parola chiave funzioni meglio per il posizionamento della tua pagina di categoria. :)
È la differenza tra:
- www.thesmoothestore.com/collections/dachshund-gifts
- www.thesmoothestore.com/dachshund-gifts
Google preferisce il numero 2.
2. Nel tag del titolo (H1).
Il tag title, o tag H1, dovrebbe contenere la parola chiave il più vicino possibile all'inizio, in questo modo:
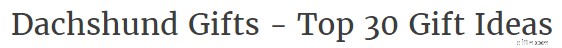
3. Nella copia del corpo.
È qui che le cose si fanno un po' più complicate. La maggior parte delle pagine delle categorie arriva direttamente ai prodotti senza presentazioni, il che non va bene per Google.
Dovresti mirare a un'introduzione di almeno 300 parole con la tua parola chiave inclusa almeno 2-3 volte. (Ma non metterlo lì dentro:fallo scorrere e sembrare naturale.)
Ecco un esempio:

4. Nel testo alternativo dell'immagine.
Poiché Google non è in grado di leggere le immagini, si affida al testo alternativo per sapere di cosa si tratta.
Questo ti dà anche un altro posto per includere la tua parola chiave nella pagina e ti dà la possibilità di apparire nei risultati delle immagini di Google.
Suggerimento professionale
Se fai schifo nel design e hai bisogno di banner realizzati per te, puoi assumere qualcuno su Fiverr o inviare una proposta a 99 Designs. Personalmente, mi piace usare Canva per creare tutti i miei progetti!
5. Nei metadati.
Sebbene l'inclusione della tua parola chiave nei metadati (il testo grigio che appare nei tuoi elenchi di ricerca) non abbia un impatto diretto sulle classifiche, può migliorare la percentuale di clic, che ha dimostrato di migliorare le classifiche.
Questo perché quando includi la tua parola chiave principale nei metadati (tag di descrizione AKA), Google la mette in grassetto nei risultati di ricerca:

Bada-bing, bada-boom. Hai finito! Facilissimo, vero?
Risciacqua e ripeti per tutte le pagine delle categorie, quindi passa alle pagine dei prodotti.
Ecco come e dove inserire tutte queste informazioni in BigCommerce per ottimizzare le pagine delle categorie di prodotti.
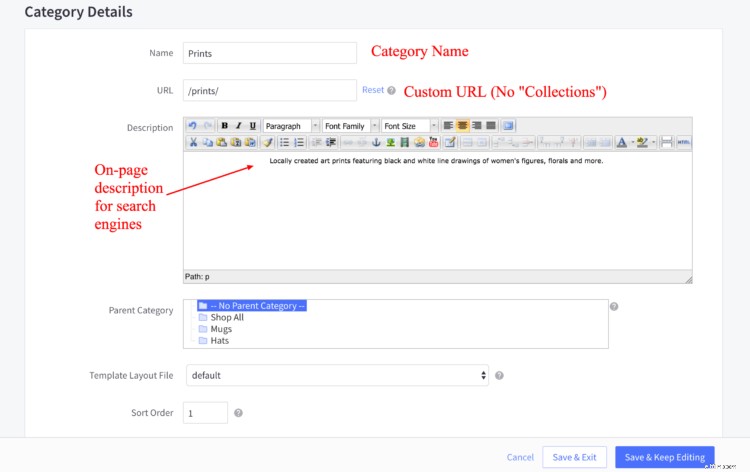
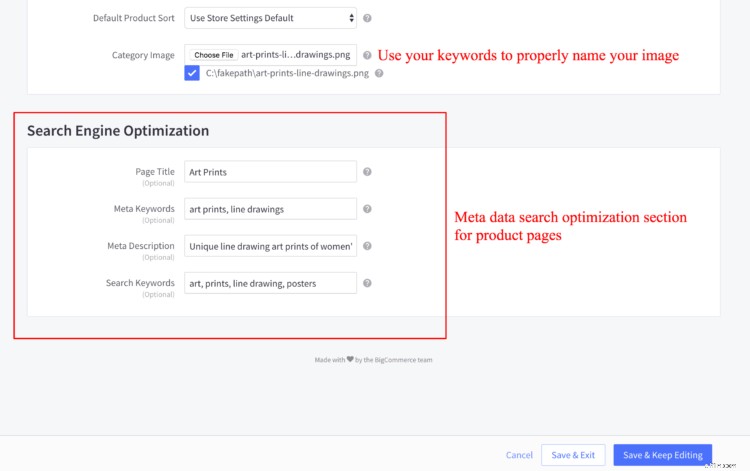
SEO on-page per le pagine dei prodotti e-commerce
Non elencherò di nuovo tutti i passaggi che hai appena eseguito sopra. Fondamentalmente, fai tutto ciò che hai appena fatto per le pagine delle tue categorie, con 2 differenze principali:
- Non hai bisogno di un'immagine banner (dal momento che hai immagini di prodotto).
- Invece di scrivere 300 parole, ti consiglio di arrivare a 1.000 parole (almeno sui tuoi 10 più venduti).
Il ragionamento è semplice:
Le prime pagine di Google tendono ad essere contenuti in formato lungo di almeno 2000 parole.
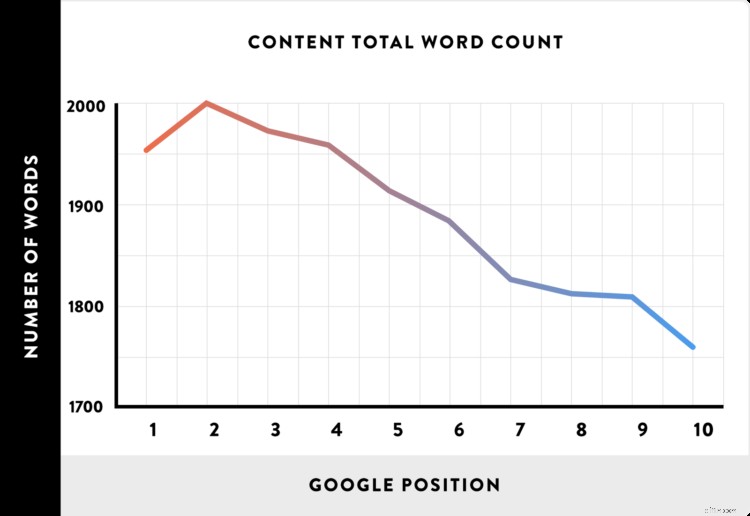
Questo perché Google è principalmente uno strumento di ricerca.
Pertanto, quando una pagina contiene molte informazioni, Google pensa di avere maggiori possibilità di contenere la risposta che un utente sta cercando.
(Questo ti aiuta anche a includere le parole chiave LSI, di cui parlerò tra un secondo.)
Quindi, se le prime pagine hanno 2.000 parole, perché ne consiglio 1.000?
Due motivi:
- Scrivere una descrizione di 2.000 parole per qualsiasi prodotto è una rottura di palle
- Le recensioni dei prodotti compensano questa mancanza di 1.000 parole
Le recensioni dei prodotti aumentano la SEO dell'e-commerce e aumentano i tassi di conversione. Se non stai già raccogliendo recensioni, inizia a dare loro la priorità!
Se hai bisogno di aiuto, ecco una fantastica guida alle recensioni dei prodotti.
Per darti un esempio di un'ottima pagina di prodotto, sia per SEO che per conversioni, dai un'occhiata a questa pagina di Solo Stove:
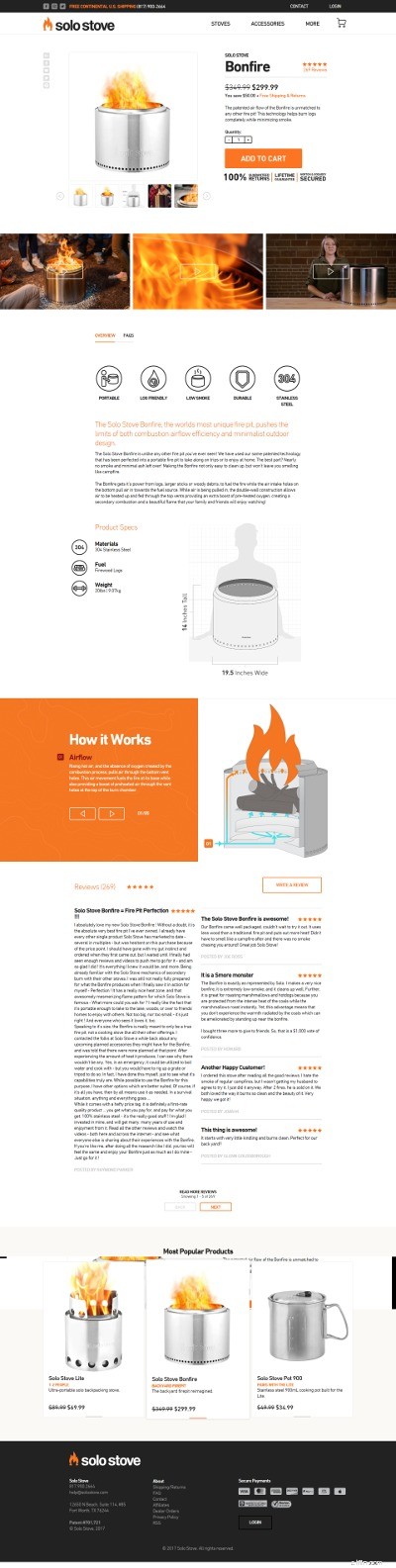
Svolgono un ottimo lavoro nell'implementazione di recensioni, contenuti di lunga durata ed eccellente usabilità, il tutto racchiuso in un design eccellente.
Cordiali saluti, se non hai un'app di recensione installata nel tuo negozio, Yotpo ha un bell'aspetto e funziona bene con i dati strutturati (di cui imparerai di più in seguito).
Of course, making massive changes to hundreds of product listings is no easy task.
To help speed this up, I recommend using a format, like this one:

During that “deep dive,” you can also include user-generated content, such as customer photos, videos or killer reviews.
For example, Spellbinders has grown traffic to their site by 130,000 unique, organic visitors by adding a gallery page pulling in user posts from Instagram to their site.
To pull everything together (and give you some more ecommerce SEO tips), here’s an infographic on optimizing your product pages by Brian Dean:
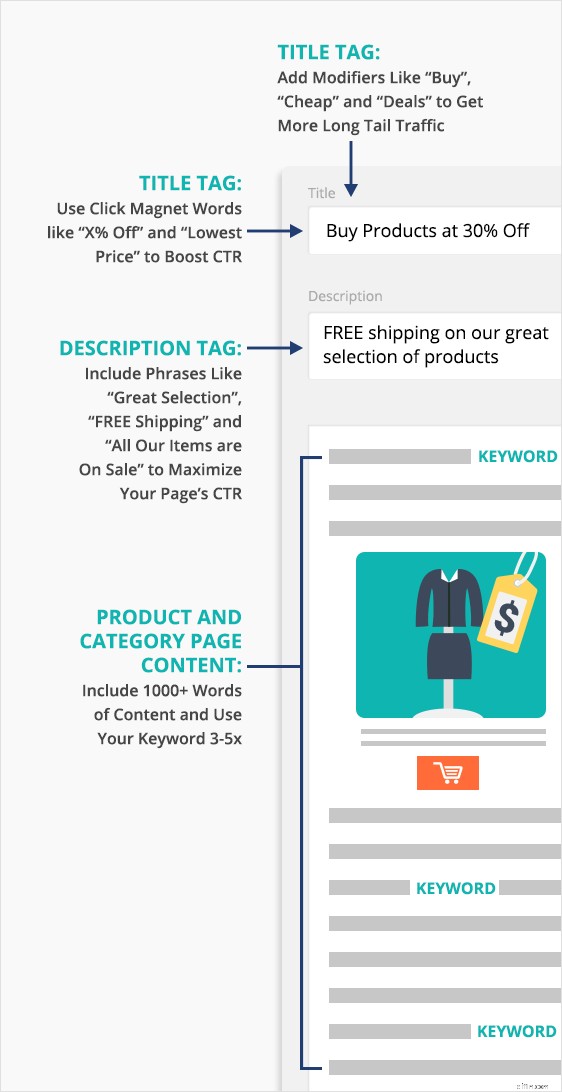
Now, back to Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords.
Before you freak out like this suddenly became an advanced math course, don’t worry! This is just a fancy way of saying “synonymous” keywords, as well as closely related keywords and topics.
For example, “dachshund,” “wiener dog,” “doxie” and “sausage dog” are all LSI keywords.
They mean basically the same thing, or are at least closely related. So are the terms “RV accessories” and “solar panels” — not because they’re synonymous, but because they fall within the same topic.
Back in the wild-west days of SEO, Google wasn’t so good at identifying the relationship between semantic keywords.
And sly SEO professionals took advantage of this.
That’s why websites used to create pages targeted to every – single – synonym.
But the game has changed, and now Google understands that when someone searches “dachshund,” it has the same intent as “weiner dog.”
So instead of creating 5 pages targeting 5 related terms, you can make one page relevant to all of them.
To find LSI keywords, you can just type your main keyword into Google and look at the auto fill suggestions…
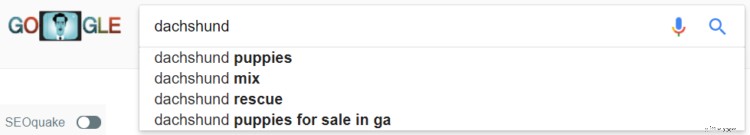
…and look at the related searches at the bottom of the page.

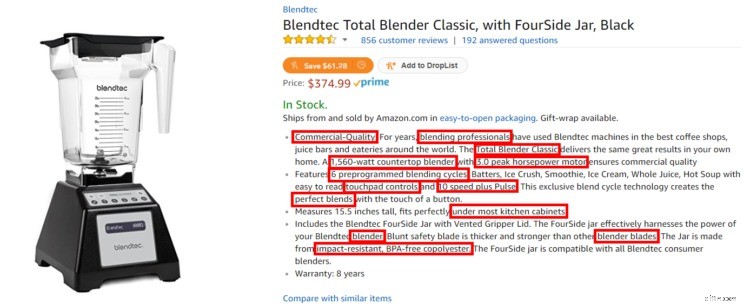
You can also check out Amazon listings for your product.
For example, when I look at this Blendtec blender on Amazon, I notice a whole slew of LSI keywords:
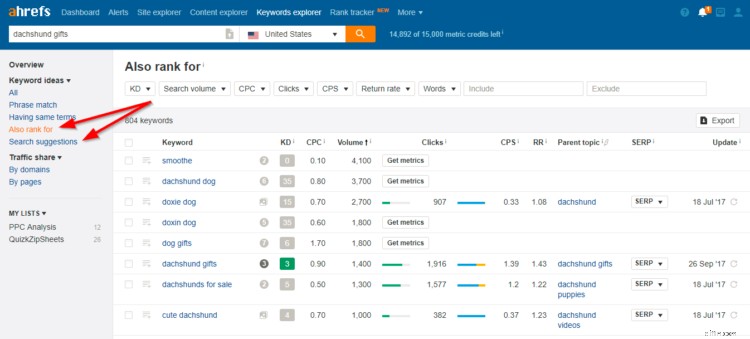
Finally, you can also use Ahrefs to find LSI keywords (told you it’s an awesome tool).
Just pop your primary keyword into Ahrefs and click on “Also rank for” or “Search suggestions” to see everything Google thinks is relevant.
Go through these two lists and grab everything that’s relevant for you. Vary your keyword usage, blend in LSI keywords and answer every question around your topic to win.
So find out your similar keywords, add them to your product pages and start ranking better for everything! :)
Suggerimento professionale
If you have a competitor that outranks you, use the same process on their site. Look for the LSI keywords they use to describe their products.
Just do this for each of your products! If you have a lot, consider starting with your best sellers and working your way from there (or hire someone to do it for you).
And make sure you have beautiful product images as well. While this doesn’t directly impact SEO, it will improve your conversions!
On to the technical side of things…
How To Perform Technical SEO Audits For Ecommerce Websites
SEO isn’t just about keywords. There’s a technical side as well, which includes things like site speed, user experience, mobile-friendliness and working links.
In the end, it’s really just about providing the best possible experience for your users.
Again, that’s what Google ultimately cares about.
So how do you perform an ecommerce SEO audit and improve your technical SEO?
I’m going to be following a very similar process to Ahref’s 16-step audit, but simplified for speed and understanding.
If you want more details, check out their full article.
Recommended Ecommerce SEO Tools
Before we get into the how-to of things, I wanted to mention the SEO tools that are highly recommended to do things right:
- Google Analytics.
- Google Search Console.
- Ahrefs.
- Beam Us Up (or Screaming Frog).
- Copyscape.
- Barracuda Panguin Tool.
- Title Tag Pixel Width Checker.
They’re not all necessary, but they make life easier. Cool? Cool. Let’s get started!
An ecommerce site audit accomplishes three things:
- It paints an overall picture of the quality and current standing of your site.
- It makes it easy for you to create a task list of things that need to be done before you focus on off-page SEO.
- It ensures you’re getting the best possible results with the least effort.
Obviously, it’s something you should need to do. So here we go.
Step 1:Crawl your site.
Using a tool like Beam Us Up (free) or Screaming Frog ($150 per year) to crawl your site is the single most important part of any site audit. It will reveal things like:
- Broken links on your site
- Missing alt text or metadata
- Thin or duplicate content
These things are all bad for SEO. So start this crawl and let it run in the background while we take care of a few other things (the crawl could take a while if you have a large site).
Step 2:Make sure only 1 version of your site Is browsable.
There are multiple ways a person can link to or browse your site:
- http://yourdomain.com
- http://www.yourdomain.com
- https://yourdomain.com
- https://www.yourdomain.com
Only one of these should be browsable.
The others should be 301 redirected to the canonical version (the one you prefer).
If possible, choose the HTTPS version (which is the secured/encrypted version) since there’s a slight search-rankings boost. Whether you want www or not is up to you.
PSSST:BigCommerce automatically does this for you.
Using HTTPS across your website is important for both your user experience and Google’s ranking algorithm.
You provide users confidence and security with your brand using HTTPS, and Google favors your site since it is secure.
An SEMrush study found that approximately 60-65% of websites with HTTPS rank on page one of Google.
Here is a handy infographic from SEMrush showing the 10 HTTPS implementation mistakes that you should fix on your site now.

Step 3:Check your home page’s SEO.
To do this, just ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the page contain a well-crafted, clickable title? Does it conform to the on-page SEO best practices you learned above?
- Is there a custom meta description? Is it optimised for maximising click-throughs?
- Is there one instance of the H1 tag?
- Are subheaders (H2, H3, etc.) properly used and conforming to SEO best practices?
- Is your target keyword included in everything above?
If you answered “no” to any of these questions, go fix that.
Suggerimento professionale
The meta title, or title tag, of a page should be no more than 512px (roughly 55 characters). Otherwise, it gets truncated, or cut off, in search results. Check your page title using the Title Tag Pixel Width Checker mentioned above!
Step 4:Analyze your crawl report.
Once your crawl report is finished, it’s time to take a look. I used Screaming Frog, but Beam Us Up looks similar:
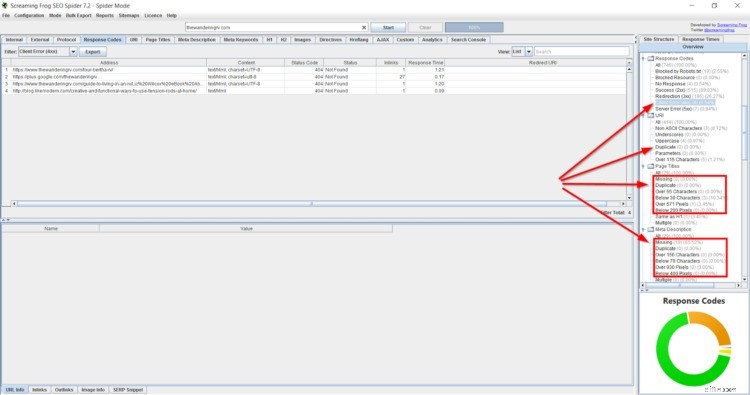
Basically, you’re looking for “Client Errors (4xx)” (aka broken links), duplicate URLs, missing or duplicate content, missing or duplicate meta descriptions and missing alt text.
If you need more help with Screaming Frog, this guide is fan-freaking-tastic.
Step 5:Ensure unique content.
Google hates duplicate content and it can get you whacked with a penalty ever since Google’s Panda algorithm update.
You can easily find potential duplicate content issues across the web with a premium Copyscape account. For $10 you can check up to 200 URLs using their batch tool.
Just grab the URLs from your report and paste them into the batch analyzer.
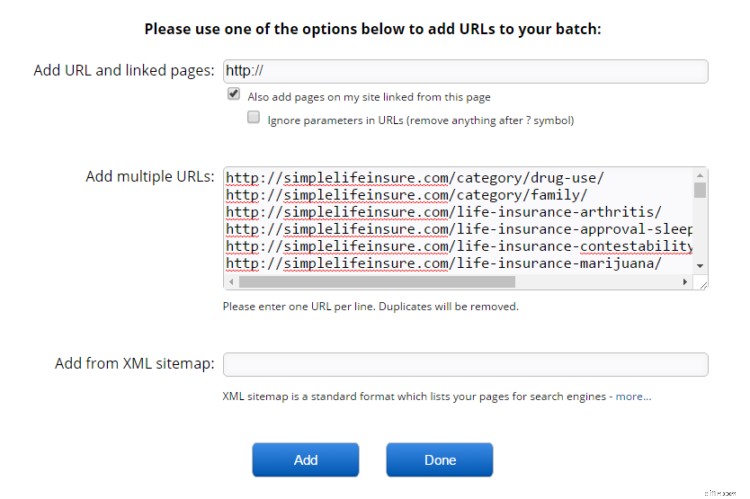
When it’s done, you’ll get a list of all the URLs with the number of duplicate content and a color-coded “risk” score.
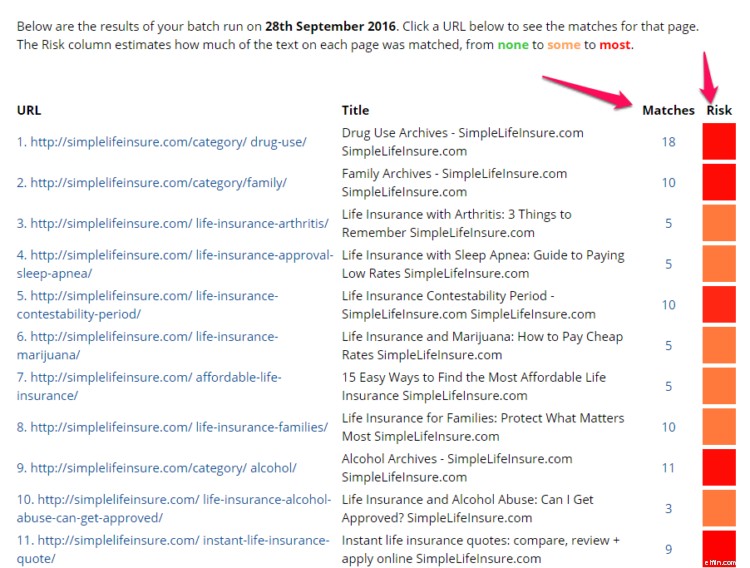
Just click the individual URLs to find the culprits. If it’s other content on your own site, change it to make it unique.
If it’s on another site, consider contacting the site owner about it or asking them to link to your original canonical URL.
Step 6:Search for yourself on Google.
First, search Google for your brand name.
Unless you’re a brand-new business, you should be the first search result. If not, that’s a sign of bigger problems.
If you’re not first, some steps you can take to resolve the problem include:
- Building a few strong, branded links (see the link-building section)
- Building some citations on business directories (see the local SEO section)
- Making sure your site has a Google Business listing (see the local SEO section)
- Ensuring your site has a presence on all major social networks
Suggerimento professionale
Speaking of social networks, you can use a tool like Narrow.io to help you grow your Twitter account on auto-pilot. Pretty cool, right?
Next, perform a search using the “site:” operator. For example, “site:bigcommerce.com”:
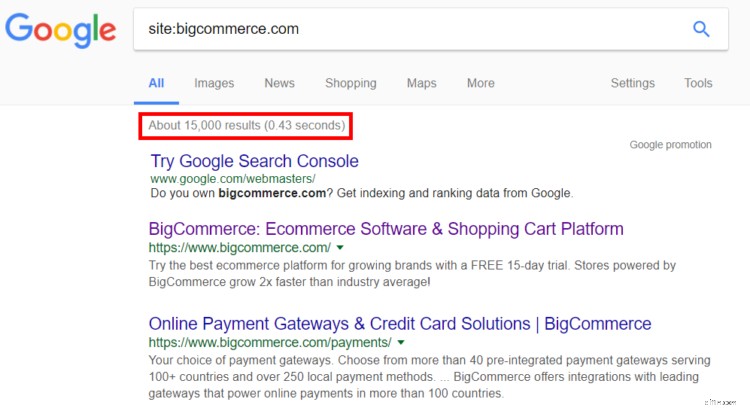
This will show you how many pages on your site have been indexed (in this case, 15,000).
This should be fewer than the number of URLs in your crawl report. If there are more, that could signal junk pages being categorized, such as product or site searches, blog category pages, or tag pages.
These pages typically have no content on them and should be noindexed (this tells Google not to index them in search results).
This will free up your site’s crawl budget — the number of pages and speed with which Google crawls your site.
Step 7:Analyze search traffic.
Take a look at your Google Analytics reports from the beginning of your site’s creation until now.
This will show you if your site was potentially hit with a penalty.
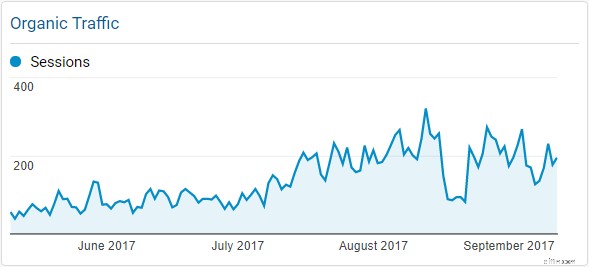
In this case a red flag would be the sudden drop and rise between August and September; however, I happen to know that was due to a redirect looping issue where the page broke.
Easy fix.
Suggerimento professionale
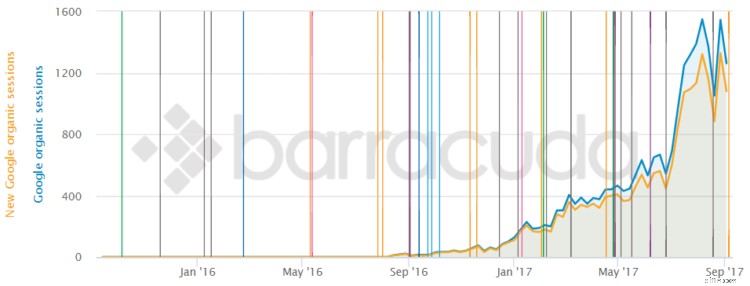
You can actually use the Panguin SEO Tool to compare your analytics against algorithm updates to see if you may have been penalized. Each of those lines correlates with a Google update. Neat-o!
Step 8:Review Google Search Console.
Google Search Console (formerly Webmaster Tools) has lots of great info for our SEO audit.
First, go to Crawl -> Crawl Errors to find any errors Google’s indexing robots are having crawling your site.
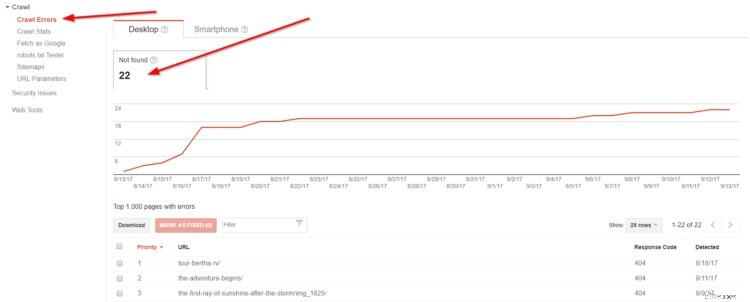
Looks like I have 22 “404 Not Found” errors — in other words, links pointing to a page that isn’t there.
I actually deleted a lot of these pages, thus why they can’t be found. You may also get this from old products no longer on your store.
The best thing to do here is redirect those old pages to related product pages, or category pages (or blog posts, if you have broken blog posts).
Next, go to Search Appearance -> HTML Improvements to find any on-page issues Google found.
This will show things like duplicate content, which you should have picked up already in the crawl. But it doesn’t hurt to double-check!
Step 9:Analyze your backlink profile.
Your backlink profile is just a way of analyzing the links pointing to your site. You want to do this to ensure you’re not getting spammy links that could get your site penalized.
To perform a backlink profile analysis, log in to Ahrefs, search for your site in their Site Explorer, then click “Backlinks” in the menu on the left-hand side.
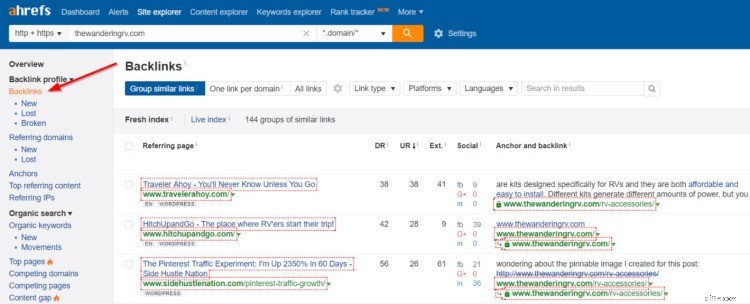
There are three things you should pay attention to here:
- Anchor text (the text that is linked to your site)
- Broken backlinks
- Sleazy links
Let’s start with anchor text.
You can see your anchor text distribution in the overview section of your site’s report, not in the backlink section.
You should see a good variety, as opposed to a lot of one word or one phrase (unless it’s your brand name, which is fine).
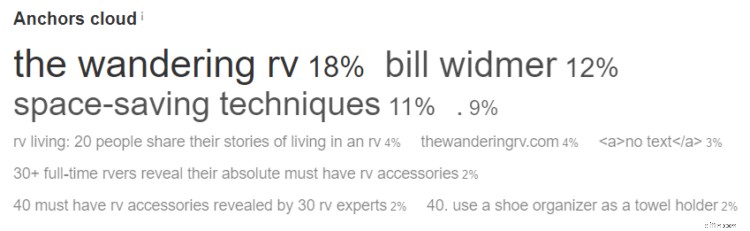
Looks like my two biggest are “The Wandering RV” (my brand name) and “Bill Widmer” (hey, that’s me!).
This is fine.
However, notice how 11% of all my links have the anchor text “space-saving techniques”. This is because I wrote an article for Lifehack with that backlink, then over a dozen other sites copied the text and stole their blog content.
This could actually hit my site with a penalty. If those sites that copied are low-quality, I should disavow those links (essentially telling Google not to follow them) to avoid a penalty.
Next up, we have broken links (aka easy wins!).
To see your site’s broken backlinks, go to Backlinks -> Broken.
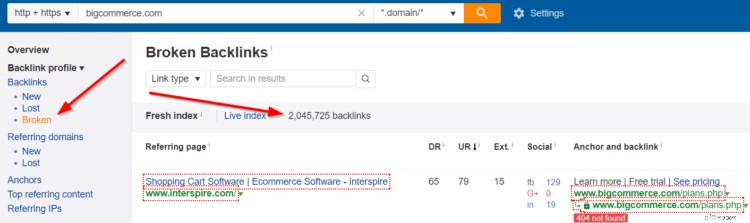
Looks like BigCommerce has over 2 million broken backlinks! Lots of potential for scoring some “SEO juice” there. :)
The best thing to do here is to either create a 301 redirect from that page to another relevant page OR contact the site owner and ask them to change the link directly to a more relevant, existing page.
While the latter is a little more powerful (since redirects lose a little “link juice”), it’s waaaaay more time-consuming.
Finally, let’s talk about sleazy links.
By sleazy links, I mean links from low-quality sites that are spammy, like the ones I mentioned pointing to my site above.
Again, these can cause Google to penalize you because they may see those links as a PBN (Private Blog Network) or other nefarious black hat tactics.
To find them, just go back to your Backlinks overview and sort the results by DR (Domain Rating) lowest to highest.
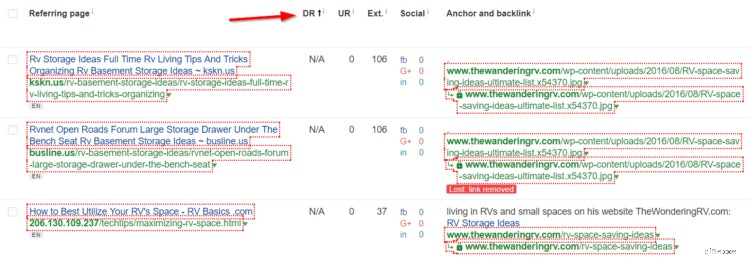
All these links with a DR of “N/A” and a UR of 0 are usually crap. Look for spammy sounding URLs and crappy websites whenever you click to view them.
Step 10:Find opportunities to improve site speed.
Site speed AND crawl speed are both important to your site’s ability to rank and user experience. According to a study from Radware, 51 percent of online shoppers in the U.S claimed if a site is too slow they will not complete a purchase.
To get an idea of what you can do to improve your site’s speed go to Google’s PageSpeed Insights Tool and plug in your URL.
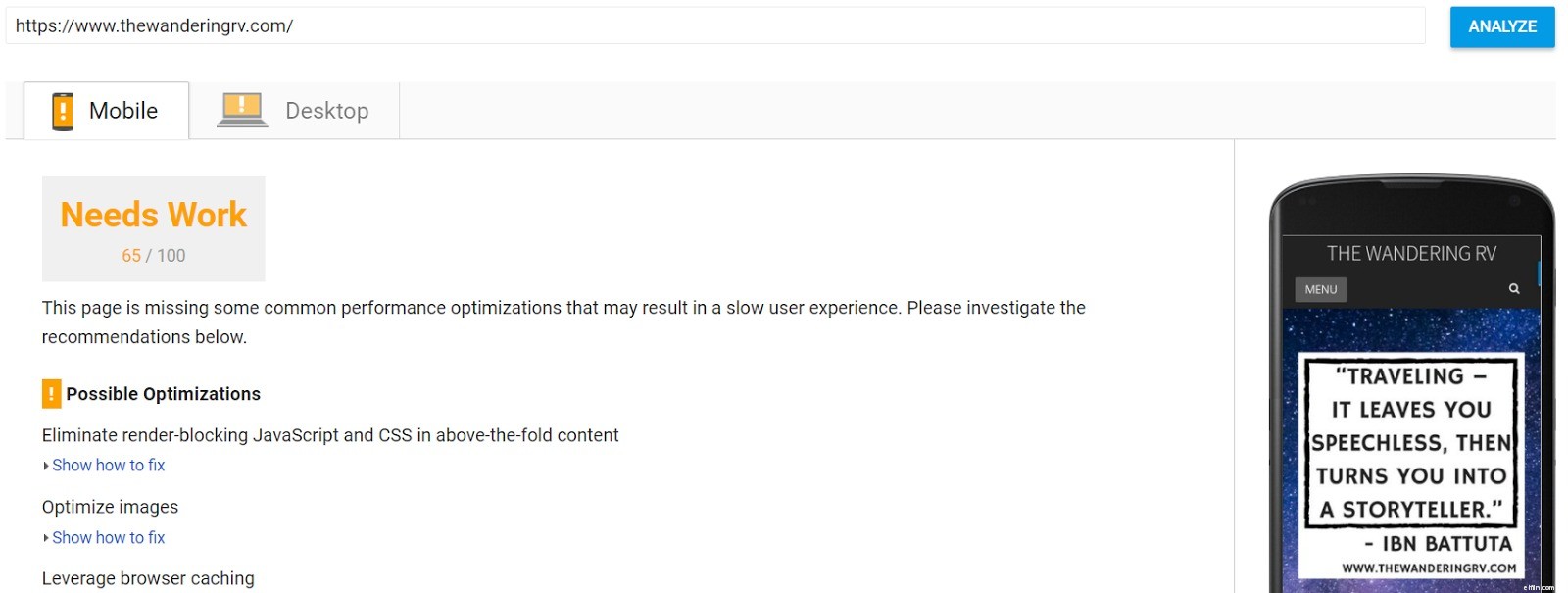
Google will score you on Mobile and Desktop from 1 to 100, and give you steps to speed things up. Check out this guide to improving your site’s speed.
However, if you only do one thing, compress your images. Image file sizes can get massive and slow things down, so this one step can make a huge difference.
Fortunately, BigCommerce takes care of this for you by using the built-in Akamai Image Manager.
E questo è tutto! You’re done with your ecommerce SEO audit. Give yourself a pat on the back — this was a lot to take on!
(Keep in mind there are a few other things you can do, like testing your site’s structured data and performing a content gap analysis, but those are for another guide.)
Now let’s move on to local SEO!
Local SEO for Ecommerce Retailers
While not applicable to everyone, if you have a physical store or just want more local site traffic, local SEO can give you a nice boost.
In this section, I’ll cover two things:
- Claiming your Google My Business profile.
- Building local citations.
- Get local links.
Simple, right?
1. Claim your Google My Business Profile.
Google has a cool feature called Google My Business, which allows you to put your business’s details into Google’s database.
This does a few things, but it mainly allows your business to show up in local search results.
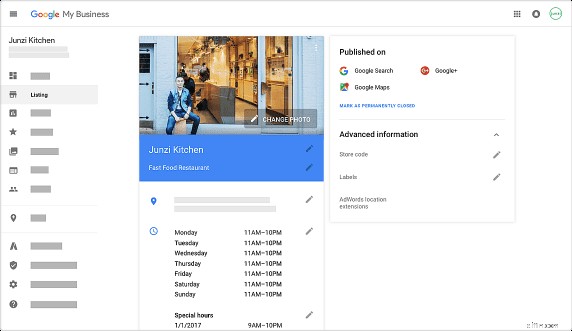
You can show your website information, address, hours of operation, pictures, reviews and more. It’s worth checking out!
But if you really want to show up in local results, you’ll need some local citations.
2. Build local citations.
Local citations are essentially backlinks from other local websites, like news outlets, magazines, press releases and other local media.
For example, claiming your free listing on Yellow Pages would be a local citation.
Citations are important for local SEO because it shows Google that you’re popular in your area.
Just as backlinks help SEO in general, backlinks from local sites help local SEO.
This also works with international SEO. If you want your site to rank higher in Australia search results, but your site is hosted in the U.S., you’ll need more links from Australian sites.
If you really want to rank, you should even consider creating separate sites for each country you are in like Neon Poogle did:
- Neon Poodle AU. http://www.neonpoodle.com.au/
- Neon Poodle US. http://neonpoodle.co/
- Neon Poodle UK. http://neonpoodle.co.uk/
3. Get links on local websites.
Any local links are a great way to build overall domain authority and help local rankings.
Quick wins include local news outlets, charities you support, locally-based blogs and any local associations such as a Chamber of Commerce.
If you’re ready to get serious about local SEO, check out Moz’s guide to building citations.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is my personal favorite kind of marketing. There’s the stats…
- 45% of marketers say blogging is their #1 strategy
- 70% of people would rather learn about a company through an article than an advert
- 68% of consumers feel more positive about a brand after consuming content from it
…but there’s also the fact that content is one of the easiest ways for your store to rank for more keywords and build more backlinks.
Think about it – your product and category pages can only rank for so many keywords. Once you’ve maxed those out, you’re not able to cover any more search real estate, so to speak.
Content fills in those gaps. Now you can rank for keywords like “best [insert your product here]”, “how to use [your product]”, and other long-tail keywords that relate to your industry.
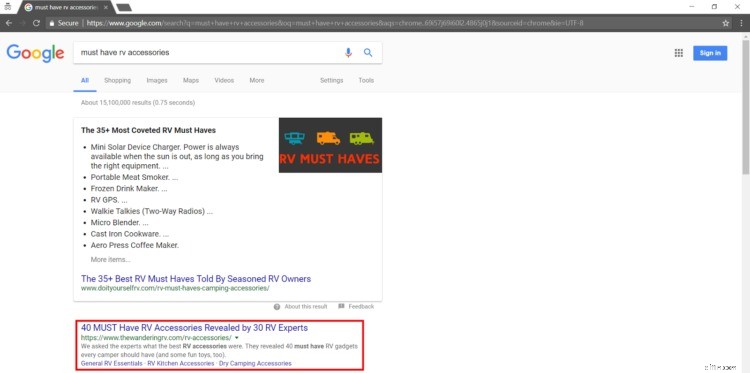
For example, I wrote a blog post about the best RV accessories for my blog, The Wandering RV, which now ranks #2 for its keyword.

Once I start selling RV accessories, I can link that page to my product pages and convert more traffic!
Not only does content marketing increase your traffic — and ultimately your sales — it also makes it easier for you to build links to your site and increase your domain authority.
Trust me when I say it’s a lot easier to build links to high-quality blog content over a product or category page.
So how do you do it?
I suggest you check out this guide — it will walk you through everything from finding the right keywords and topics to writing the content, promoting it and building links!
Alternatively, if you prefer listening to content, check out my podcast episode with Kurt Elster.
I walk you through everything step-by-step so you know exactly how to grow your ecommerce store with content marketing!
Now, we’re finally on to the most important part of SEO…
Link Building For Online Retailers
There are two ranking factors Google cares about more than anything else…
- Content.
- Links.
Backlinks from other websites with high domain authority to your website improves your rankings more than nearly any other ranking factor.
Because they are considered off-page SEO, it’s a little more complicated and time-consuming than simply making a tweak to your website.
Instead, you’ll need to collaborate with other bloggers and website owners to acquire those links.
We’ll talk about four unique link-building opportunities:
- Resource page link building.
- Partnering with influencers.
- Broken link building.
- Stealing competitors links.
While these aren’t the only link-building methods, they’ve been the most effective for me and the easiest to learn.
Immergiamoci!
1. Resource page link building.
Resource pages are, for lack of a better definition, pages full of resources around your industry.
They might take the form of a blog post, like this:

Or a static page, like this:

While the latter may not give you a ton of page authority due to the sheer number of links on the page, they are much easier to get and give you some boost in your rankings.
In order to find resource pages, just Google “inurl:resources + X” (X being your product, topic, or industry).
For example, when doing this for my RV blog, I searched “inurl:resources + RV”.
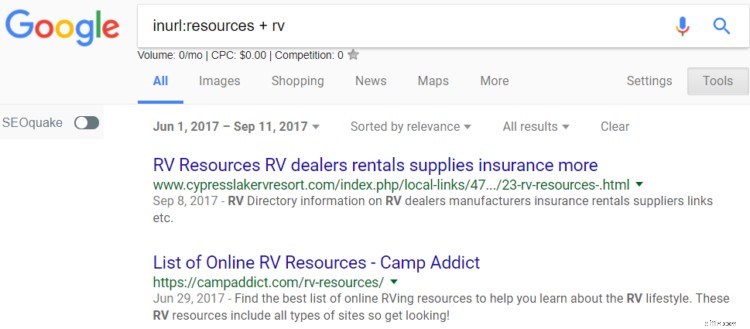
Once you find a promising page, add the URL and the site’s contact info to a spreadsheet. You can find contact info quickly using a tool like Voila Norbert.
Once you have a good list of leads, it’s time to send them an email. You can use a template (like the one below), but make sure you customize each email and don’t sound robotic.
Honestly, sending lots of these outreach emails sucks. But it’s the most important step in SEO, and it works.
If you want a hack to save time, I use MailShake to send mass custom emails really quickly. (My record is 100 emails in 45 minutes!)
But don’t forget; there are other ways to build links!
2. Partnering with influencers.
Influencers are people in your industry or niche who have a large following and/or a website with a high domain authority but aren’t competing with you directly.
You’ve probably heard of influencer marketing. Partnering with influencers for SEO is a little different, however.
Rather than paying an influencer to share your product on social media, the goal is to get them to link back to your site from their site. This could be a blog post featuring your products, or just getting a link from an existing page on their site.
For example, I used this method to get a link at the bottom of an existing article from Heath and Alyssa, two of the most popular full-time RV bloggers:
I actually met up with them in real life and linked to their blog several times. But you don’t need to go through that much effort to get a link most of the time. Instead, just focus on building friendships with influencers.
How can you do that?
- Share and comment on their content
- Send them customers
- Reach out to them and ask questions about their expertise
- Give them free products or other gifts
- There are tons of other ways — just think of it as befriending someone. How can you be that person’s friend? Do more of those things.
There are tons of other ways — just think of it as befriending someone. How can you be that person’s friend?
Do more of those things.
If you’re looking to find more influencers, check out this list of people who are open to partnerships.
Alternatively, you can just start performing Google searches for “[your topic] blogs/influencers”. They’re easy to find – that’s what makes them influential!
3. Broken link building.
Also called “building links by fixing the internet,” broken link building is one of the most effective and easy link building tactics.
Funziona così:
You use a browser extension like this one to search websites in your niche for broken links. You can check resource pages for a double-whammy, or just check blog posts around your topic.
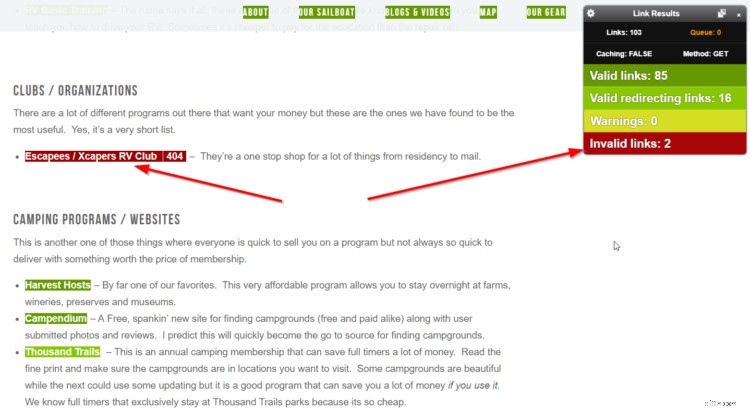
Any broken links appear highlighted in red, so they’re easy to spot. Once you find one on a site, email the owner something like this:
OR
And that’s all there is to it!
Just keep in mind that you’ll probably need to send a few hundred emails just to get a handful of links, unless you’re a link building genius of some kind.
(Ain’t nobody got time for that. Hire me to do it for you!)
4. Stealing competitors links.
How would you like to improve your rankings while simultaneously pushing out the competition?
Well, you can! All it takes is our handy dandy SEO tool:Ahrefs.
Just as you can use Ahrefs to spy on your competitor’s keywords, you can also use it to find out where they’re getting all their links from — and try to steal them for your own!
Here’s how:
- Plug in their URL into the site explorer.
- Click on the “backlinks” tab on the left-hand side.
- Filter by “One link per domain” and link type “Dofollow” (Dofollow links tell Google to follow them, nofollow links tell Google not to follow them).
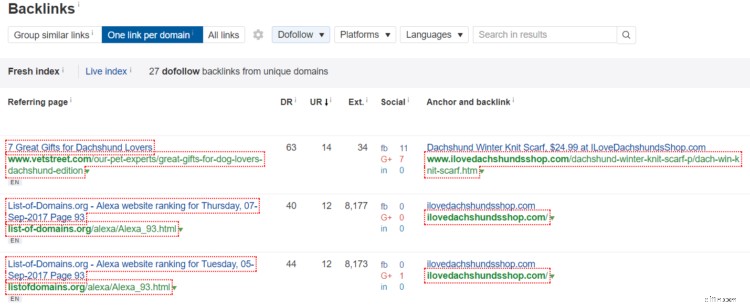
Now you can see exactly where your competitors are getting their links, and to what pages. Neat-o!
So how do you steal them?
Well, it depends on the link. If they’re in a blog post — like the “7 Great Gifts for Dachshund Lovers” in the example above — you can just reach out to the owner and try to be included.
Suggerimento professionale
Send them a free gift to boost your chances!
If the link is coming from a resource page, reach out just like you normally would. If it’s from the navigation in a site, reach out and see if you can be added as well or replace the other person — they might have a deal worked out where the linkee is giving the linker free gifts or a commission or something.
See if you can partner with them yourself!
Speaking of commissions, you should definitely consider starting an affiliate program to boost your sales and SEO. It’s practically free money!
And that wraps up our section on link building. But how do you know if this stuff is even working?
Measuring SEO Success for An Ecommerce Website
If you’ve ever wondered, “How do I know if my SEO efforts are working?” you’re not alone.
SEO isn’t as cut and dry as PPC — you can’t immediately calculate ROI after a day of ad spend.
Instead, the signs are more subtle and take a longer time. But what are the signs?
Small increases in rankings.
In order to track your rankings, there are two things you can do:
- Use an SEO tool like Ahrefs to track them.
- Create an SEO dashboard in your analytics account.
I recommend doing both, if possible, but only the second method is free. Let’s discuss them!
1. Use Ahrefs to track search rankings.
Ahrefs has a built-in rank tracking feature you can use to be notified whenever your rankings increase or decrease.
In fact, they just enhanced this feature to give even more useful information, like comparing your progress to your competition and seeing your overall search visibility!
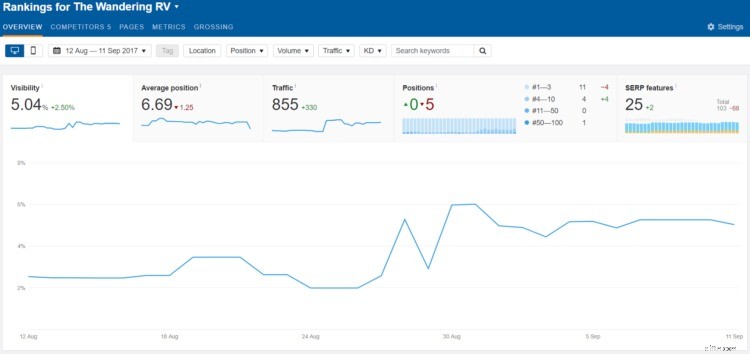
While I’ve found it’s not 100% accurate, it does give you a general sense of whether your rankings are overall going up or down.
What you’re looking for is a general increase, even a small one, in your rankings for your targeted keywords over time.
Personally, I like to check rankings at least once a week to look for this change, but it can take a few months to really see the fruits of your labor.
2. Use Google Analytics to measure organic traffic and engagement metrics.
If you want a free method to see search ranking improvements, or just want more data (which can’t hurt), install this free SEO dashboard to your analytics.
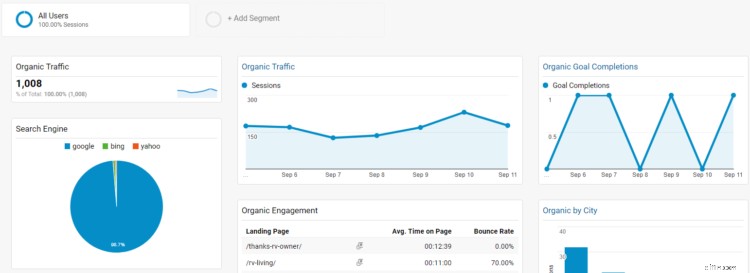
Here, rather than looking for direct ranking improvements, you’re looking for more subtle clues…
- Increases in search traffic
- The landing page that search traffic is reaching
These two pieces of information can be used to determine which keywords you’re ranking for
Then, you can perform an incognito Google search to see where you’re at (incognito mode keeps Google from using your personal search history to change results).
Once you’ve found yourself, you know where you stand — if you’re not using Ahrefs, make a note of your current position so you can track it over time.
Again, you’re looking for slight increases. If you go from page 5 to page 2, that’s a big hint you’re doing something right and your efforts will soon pay off.
It’s also important to measure where your organic traffic is coming from:desktop or mobile?
SEMrush discovered that for certain ecommerce verticals the percentage of organic traffic can vary.
Desktop vs Mobile Organic Traffic by Ecommerce Verticals
Desktop performs well in:
- Health is 60.65% of traffic
- Furniture is 59.59% of traffic
- Food/Nearfood is 58.75% of traffic
- Children is 58.34% of traffic
Mobile performs well in:
- Electronics is 44.78% of traffic
- Jewelry is 44.7% of traffic
- Travel is 44.11% of traffic
- Flowers is 42.85% of traffic
For ecommerce, people tend to perform research on desktops. Preliminary research may be done on mobile but this also leads to more desktop searches.
This is important because you want your pages to be optimized for the best visitor experience.
Google is moving toward a “mobile-first” index so all ecommerce sites should makes sure their sites are optimized of this major change moving forward.
And that’s about all there is to it!
Give yourself a big pat on the back; this was a pretty dense read.
Be sure to come back to this guide to ecommerce SEO often, as you can’t do it all in one go!
Before I leave you, though, I’d like to inspire you with a few ecommerce SEO case studies.
Ecommerce SEO Case Studies
Just to help you see what’s possible and get you excited, I wanted to share some success stories.
Specifically, these:
- How one ecommerce site increased their search traffic by 1780%
- An ecommerce SEO strategy led to a 64% increase in organic revenue
- Ecommerce site sees 400% traffic increase with generic SEO keyword effort
- This ecommerce store went from 35,000 to 225,000 organic visits per month
Rather than running through each individual ecommerce SEO case study, I’ll just give you an overview on how they did it.
How to perform an update and optimize your SEO:
- Find your best keywords (both commercial keywords for your product and category pages, and long-tail keywords for your blog content).
- Match the right keywords to the right pages on your site.
- Optimize your site by performing an SEO audit, fixing your site’s architecture (if it’s not ideal), reducing thin content and doing everything you can to optimize your crawl budget.
- Enhancing your site’s on-page SEO and creating or updating content to be the best result for its target keywords, being sure to link back to your most important product pages.
- If necessary, building white-hat links to your most important pages.
- Sit back and watch as the money starts pouring in!
That sounds oversimplified — and in some ways it is — but SEO is often unnecessarily complicated.
Just remember that Google’s goal is to provide the best possible search results, so if you make that your goal, you’ll win in the long run.
Riepilogo esecutivo
There are only so many ways to get traffic — social media, paid ads, email or search.
Search traffic is the only one of these ways that’s reliable, free and fairly easy to get.
If you want your site to get hundreds, thousands or even hundreds of thousands of monthly visitors, you need to learn ecommerce SEO today.
A simple SEO campaign can result in hundreds of extra sales. And it doesn’t have to take you years to achieve, either.
Follow the steps in this guide and you’ll be leagues above your competition. You’ll start to rank on the first page — and even in the top 3 results — for all your shop’s main keywords. It really is a no-brainer.
If you found this guide helpful, please take a moment to share it so we can help as many store owners as possible grow their business!
And if you’re feeling overwhelmed or don’t have time for all this SEO stuff, reach out to me. I’m more than happy to help! :)
Do you have any questions or know other ecommerce SEO best practices? Leave a comment below! Let’s keep the conversation going.
Attività commerciale
- Come contrattare il negozio
- La guida definitiva alle vacanze e-commerce 2021-2022 (e modello gratuito)
- 30 modi comprovati per indirizzare il traffico e le conversioni di e-commerce al tuo negozio online
- 14 idee di business per l'e-commerce da testare nel 2022 (+ come iniziare)
- Come ottimizzare le immagini dell'e-commerce per aumentare le vendite:una guida alla SEO e alla conversione delle immagini
- E-commerce del vino:come vendere con successo vino online (include i regolamenti di spedizione per stato)
- La strategia dei contenuti per triplicare il traffico e-commerce (ed esattamente come farlo)
- Come evitare e gestire il conflitto del canale di e-commerce B2B
- In che modo la personalizzazione può ridurre le frequenze di rimbalzo dell'e-commerce del 20-30%
- Guida il tuo marchio (+ traffico online) con il piano di marketing e-commerce perfetto
-
 Come eseguire un'analisi di pareggio:una guida del 2022
Come eseguire un'analisi di pareggio:una guida del 2022 Un must per le piccole imprese e per coloro che stanno pensando di entrare in affari, unanalisi di pareggio ti consente di sapere quando puoi aspettarti di iniziare a guadagnare un profitto. Uno dei ...
-
 In che modo la tua banca può aiutarti a diventare senza carta?
In che modo la tua banca può aiutarti a diventare senza carta? Le banche dovrebbero fare di più per aiutarti a diventare totalmente senza carta? Guarda altre foto bancarie. Non è unesagerazione affermare che la maggior parte delle persone che pagano bollette e h...


